|
Puregon What you should know about Puregon Please read the following information carefully before using this medicine. The leaflet contains details about Puregon, as well as some general advice on using medicines. If you have any questions or other concerns, please ask your doctor or pharmacist. Name of your medicine The medicine prescribed for you is called Puregon. Composition and strength - what your medicine contains Puregon contains a hormone known as follicle-stimulating hormone (or FSH) in a strength of 100 I.U. per ampoule. Besides FSH, the powder contains sucrose, sodium citrate, and polysorbate 20- the solvent contains sodium chloride (4.5 mg) and water for injections (1.0 ml). Pharmaceutical form - what your medicine consists of Puregon 100 I.U. is supplied in a glass ampoule as a dry powder, which should be dissolved with the solvent contained in a second glass ampoule. It is available in packs of 1, 3, 5 and 10 ampoules. Therapeutic group - how your medicine works Gonadotropins (including FSH) play an important role in human fertility and reproduction. FSH is needed in women for the growth and development of follicles in the ovaries. Follicles are small round sacs that contain the egg cells. Marketing authorisation holder and manufacturer: Organon (Ireland) Limited P.O. Box 2857, Drynam Road, Swords, Co. Dublin, Ireland. Indications - when your medicine is used Puregon is used to treat infertility in either of the following situations:
|
Contraindications - when you should not use this medicine There are certain medical conditions in which Puregon should no be used. Do not use Puregon if you:
This medicine should not be used when a condition exists which makes a normal pregnancy impossible. This may occur with primary ovarian failure, when there are fibroids in the uterus or when certain malformations of the sexual organs are present. Special warnings and precautions for use Caution Close supervision of patients by a doctor is very important. Usually ultrasound scans of the ovaries are regularly made, and blood or urine samples are regularly taken. The results of these tests allow the doctor to choose the correct dose of Puregon from day to day. This is very important since too high a dose of FSH may lead to rare but serious complications in which the ovaries become overstimulated. This may be noticed as pain in the abdomen. Regular monitoring of the response to FSH-treatment helps the doctor to prevent ovarian overstimulation. So contact your doctor without delay if you are experiencing significant abdominal pain, also if this occurs some days after the last injection has been given. Interactions - when you are taking other medicines If Puregon is used in combination with clomiphene citrate there may be an increased follicular response. If a GnRH agonist has been given, higher dose of Puregon may be needed to achieve a response. |
|
|
Women who are not ovulating:
Treatment usually starts with the administration of 75 I.U. FSH per day. The starting dose is continued for at least seven days. If there is no ovarian response, the daily dose will then be gradually increased until follicle growth and/ or plasma oestradiol levels indicate an adequate response. The daily dose is then maintained until a follicle of adequate size is present. Usually 7 to 14 days of treatment are sufficient. The administration of Puregon is then stopped and ovulation can be induced by administering human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).|
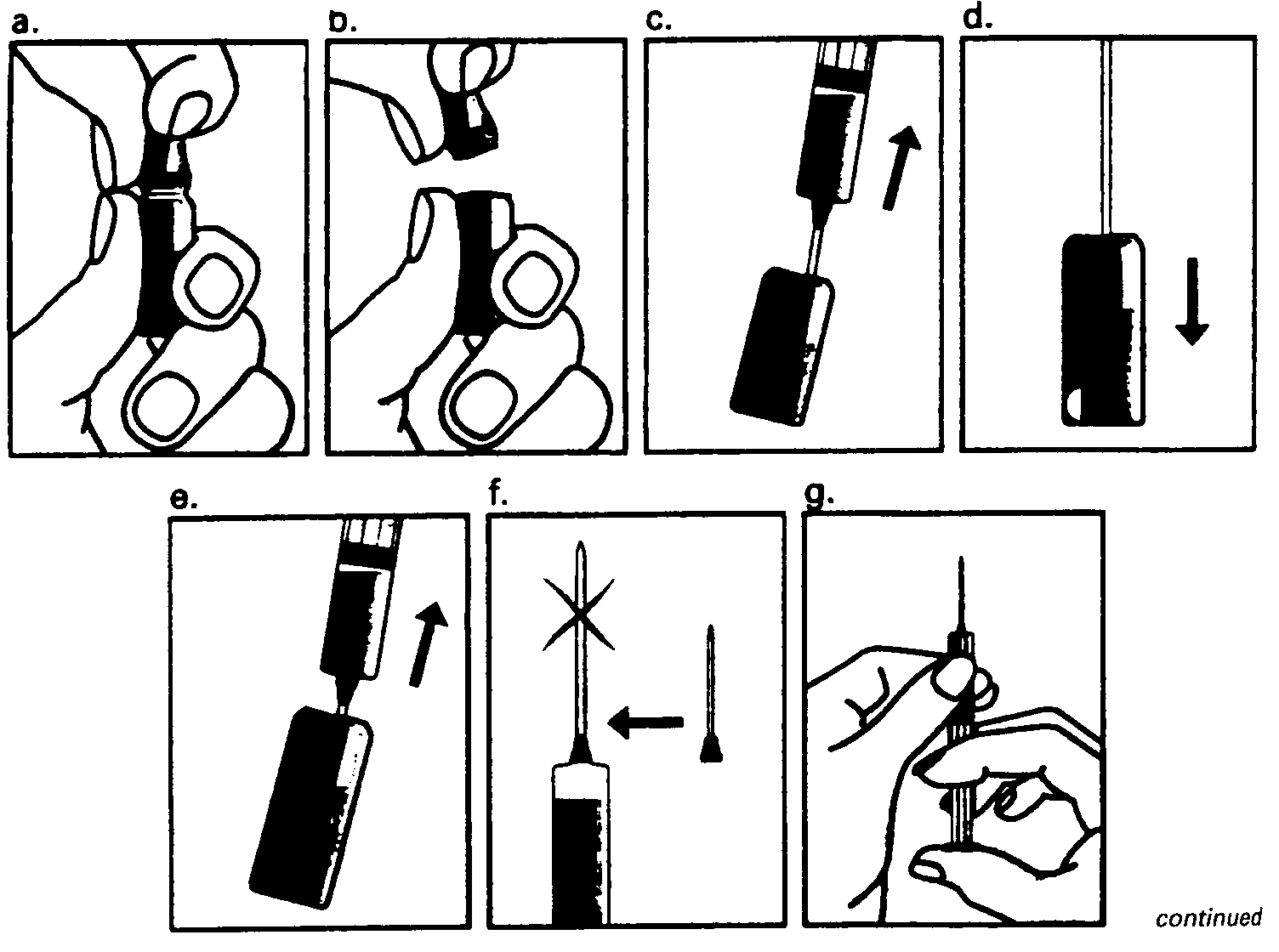
Step 5 - Checking the correct needle position If the needle position is correct the plunger should be quite difficult to draw back. Any blood sucked back into the syringe means that the needle tip has penetrated a vein or artery. If this happens pull out the syringe, cover the injection site with a swab containing disinfectant and apply pressure; the site will stop bleeding in a minute or two. Do not use this solution but flush it away. You should then start again with Step 1 using a new needle and new ampoules of Puregon and sodium chloride solution. Step - Injecting the solution Depress the plunger slowly and steadily, so the solution is correctly injected and the muscle or skin tissues are not damaged. Step 7 - Removing the syringe Pull the syringe out quickly and apply pressure to the injection site with a swab containing disinfectant. A gentle massage of the site - while still maintaining pressure - helps disperse the Puregon solution and relieve any discomfort. Any remaining solution should be discarded. Do not mix the Puregon solution with any other medicines. Overdose Too high a dose may cause overstimulation of the ovaries. See Section on Undesirable Effects below. Undesirable effects - unwanted effects A serious complication with FSH is unwanted overstimulation of the ovaries. This condition is rare, and the risk can be reduced by careful monitoring of follicle development during treatment. The first symptoms of ovarian overstimulation may be noticed as pain in the abdomen, feeling sick or diarrhoea. In more severe |
cases symptoms may include enlargement of the ovaries, accumulation of fluid in the abdomen and/or chest, weight gain and the occurrence of blood clots in the circulation. Contact your doctor without delay if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, also if they develop some days after the last injection has been given. Minor side effects include bruising, pain, redness, swelling and itching at the site of the injection. Shelf life and storage precautions - looking after your medicine Keep Puregon in the original box in a safe place out of the reach of children. Puregon should be stored below 30°C and protected from light. Do not freeze. The expiry date is printed on the box and on the label after 'exp.'. Do not use Puregon after this date. Any unused solution should be discarded. This information was last updated in December 1995. General things to remember about medicines
|